Now Reading: The Illusion of Anomaly: Three-Headed Squirrel Debunked
-
01
The Illusion of Anomaly: Three-Headed Squirrel Debunked
The Illusion of Anomaly: Three-Headed Squirrel Debunked
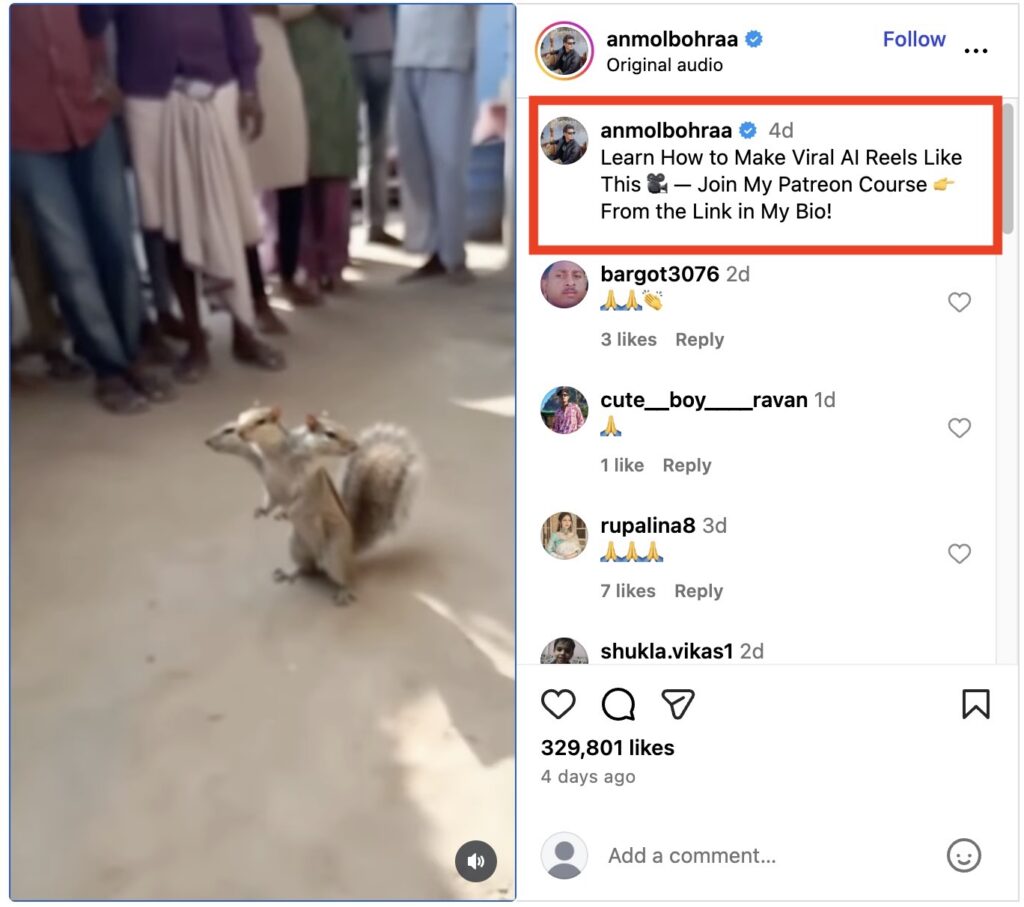
New Delhi, November 22, 2025: A video clip featuring an ostensibly three-headed squirrel was recently circulated across various social media platforms, quickly attracting widespread attention. The bizarre and scientifically implausible nature of the creature ensured that the footage was shared prolifically by intrigued users. Initial reports suggested the video was an authentic capture of a rare mutation or anomaly in wildlife. Consequently, the clip was consumed by millions of viewers who were left questioning the biological feasibility of such a specimen.
Scrutiny by Digital Experts
However, the video’s authenticity was soon challenged by digital forensics experts and tech-savvy commentators. The highly unusual appearance of the animal was subjected to rigorous analysis, whereby the visual consistency and movement were closely examined. Key inconsistencies and tell-tale signs of digital manipulation were quickly identified by specialists. These irregularities suggested that the video had not been captured naturally but had been artificially generated using sophisticated software.
It was ultimately concluded by experts that the footage was, in fact, fabricated using Artificial Intelligence (AI) technology. This determination was made based on subtle visual artifacts that are commonly left behind by advanced generative models. The way the light interacted with the different ‘heads’ and the unnatural blending of the body parts were cited as primary evidence of digital tampering. Thus, the initial biological mystery was resolved by technological debunking.
Also Read: The Quiet Congestion: Dubai’s Model Civic Sense
The Impact of Generative AI
This incident serves as a significant example of how convincing AI-generated content is becoming. Such realistic yet fictional images and videos can be created with increasing ease and are then disseminated rapidly across the internet. The video’s virality clearly demonstrated the ease with which misinformation or fabricated content can be accepted as factual by the general public before proper verification is performed. A necessary dialogue about media literacy and critical consumption of online content has been sparked by this widely shared fabrication.
The spread of the three-headed squirrel video acts as a timely reminder that visual media should be viewed with a degree of skepticism. Viewers are increasingly being asked to employ caution before accepting extraordinary claims that are supported only by unverified digital footage. The technology that was used to create this visual prank highlights the growing need for robust tools to detect and label AI-generated media.
Lessons Learned from the Hoax
Ultimately, the three-headed squirrel video has been classified as a digital hoax. The footage has been relegated to the category of synthetic media and is no longer being treated as a genuine biological observation. The public has been educated by the swift response of digital analysts who prevented the widespread acceptance of this convincing but fake anomaly. The importance of fact-checking and media skepticism has been reiterated by this viral sensation.










