Now Reading: Himalayan Meltdown: Glaciers’ Retreat Threatens Pastoral Lives, Warns UN Report
-
01
Himalayan Meltdown: Glaciers’ Retreat Threatens Pastoral Lives, Warns UN Report
Himalayan Meltdown: Glaciers’ Retreat Threatens Pastoral Lives, Warns UN Report
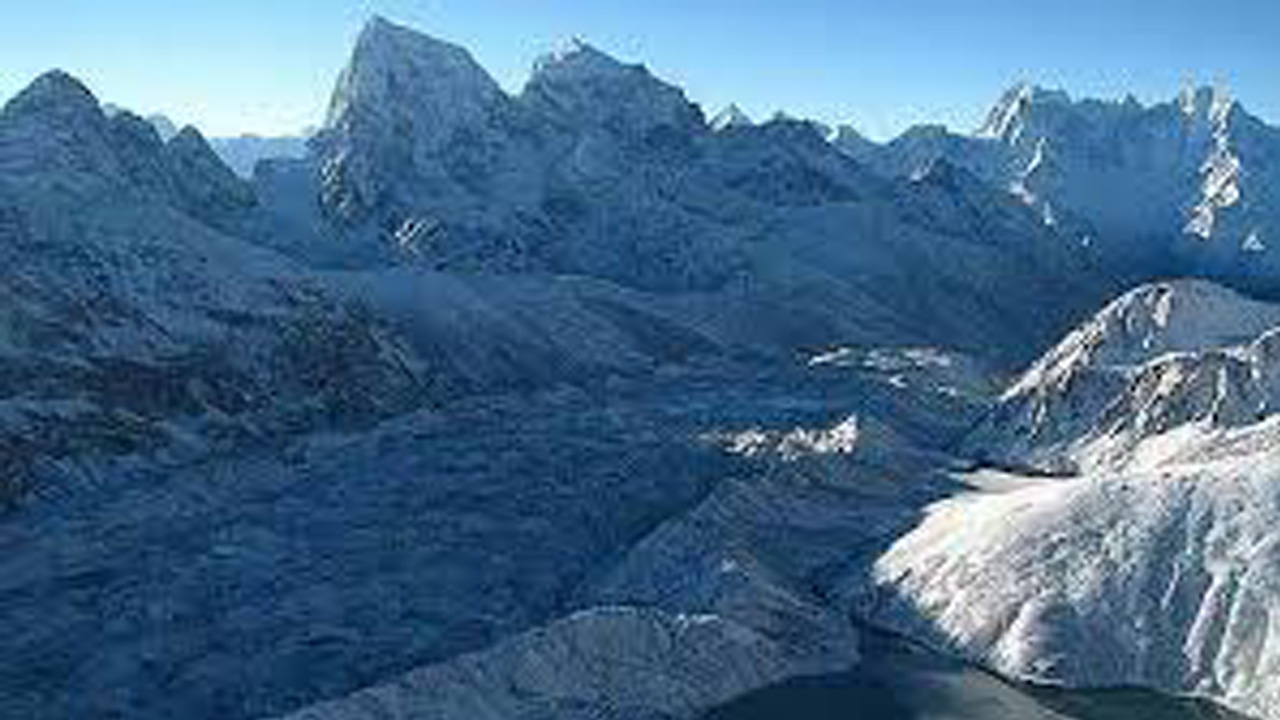

The majestic Himalayas, a lifeline for millionsare facing an unprecedented crisis. A recent United Nations report has sounded a stark alarm: the rapid melting of glaciers, driven by escalating global temperatures, is posing an existential threat to the traditional pastoral livelihoods of communities nestled within these towering mountains. This accelerating glacial retreat, a direct consequence of climate change, is disrupting age-old practices and pushing vulnerable populations to the brink.
The Himalayas, often referred to as the “water tower of Asia,” are home to the world’s largest concentration of glaciers outside the polar regions. These glaciers feed numerous rivers, providing crucial water resources for agriculture, drinking, and energy production for billions of people downstream. However, the report highlights a disturbing trend: the rate of glacial melt has significantly increased in recent decades, surpassing previous projections.
“The impact of climate change on the Himalayan region is not a distant threat; it’s a present reality,” the UN report states. “The accelerated melting of glaciers is disrupting the delicate balance of the ecosystem, with severe consequences for the communities that rely on it for their survival.”
Pastoral communities, who have adapted to the harsh mountain environment over centuries, are particularly vulnerable. Their traditional way of life, intricately linked to the seasonal availability of water and grazing pastures, is being undermined by the changing climate.
Disrupted Seasonal Rhythms:
The report points to several key challenges faced by these communities:
- Water Scarcity: Glacial melt initially increases water flow, leading to flash floods and landslides. However, as glaciers shrink, the long-term effect is a reduction in water availability during crucial dry seasons. This scarcity is impacting livestock, which require consistent access to water and pasture.
- Altered Grazing Patterns: The timing and availability of grazing pastures are changing due to shifting precipitation patterns and rising temperatures. This is disrupting traditional transhumance practices, where herders move their livestock seasonally to different pastures.
- Increased Natural Disasters: The report notes a rise in the frequency and intensity of glacial lake outburst floods (GLOFs), avalanches, and landslides, posing significant risks to human lives and infrastructure.
- Loss of Biodiversity: The changing climate is also impacting the delicate ecosystem of the Himalayas, leading to the loss of biodiversity and impacting the availability of medicinal plants and other resources that pastoral communities rely on.
The Human Cost:
The consequences of these changes are far-reaching. The report emphasizes the human cost of glacial melt, highlighting the following:
- Food Insecurity: Reduced water availability and altered grazing patterns are threatening the food security of pastoral communities, who rely on livestock for milk, meat, and other essential products.
- Economic Hardship: The disruption of traditional livelihoods is forcing many pastoralists to abandon their ancestral practices and seek alternative sources of income, often in already overcrowded urban areas.
- Cultural Erosion: The loss of traditional pastoral practices is also leading to the erosion of cultural heritage and traditional knowledge, which has been passed down through generations.
- Increased Migration: Environmental changes and economic hardship are leading to increased migration from the region, leading to population shifts and increased pressure on resources in other areas.
Urgent Action Required:
The UN report calls for urgent action to address the challenges posed by glacial melt in the Himalayas. It emphasizes the need for:
- Climate Change Mitigation: Reducing greenhouse gas emissions is crucial to slowing down the rate of glacial melt and mitigating the impacts of climate change.
- Adaptation Strategies: Supporting pastoral communities in adapting to the changing climate through the development of sustainable water management practices, improved livestock management, and diversification of livelihoods.
- Early Warning Systems: Strengthening early warning systems for natural disasters, such as GLOFs and landslides, to reduce the risk to human lives and infrastructure.
- International Cooperation: Fostering international cooperation to support research, monitoring, and adaptation efforts in the Himalayan region.
- Investment in sustainable infrastructure: Building infrastructure with climate change in mind is essential.
The rapid melting of Himalayan glaciers is not just an environmental issue; it’s a humanitarian crisis in the making. The future of millions of people, their livelihoods, and their cultural heritage hangs in the balance. The need for immediate and decisive action is more critical than ever before. The world must recognize the urgency of this situation and work together to protect the vulnerable communities of the Himalayas from the devastating impacts of climate change.