Now Reading: NCR Commuter Boom: Alwar, Panipat Corridors on Track for Approval, Meerut Project Nears Completion
-
01
NCR Commuter Boom: Alwar, Panipat Corridors on Track for Approval, Meerut Project Nears Completion
NCR Commuter Boom: Alwar, Panipat Corridors on Track for Approval, Meerut Project Nears Completion
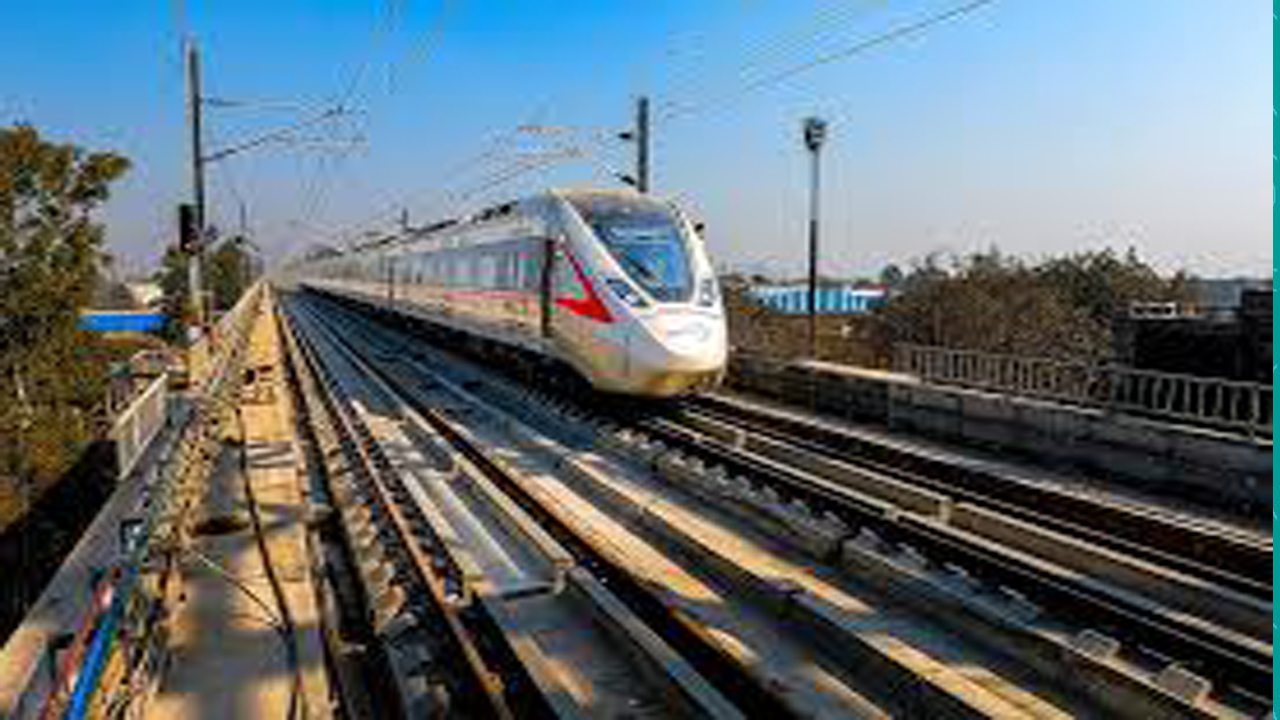

The landscape of regional connectivity in the National Capital Region (NCR) is poised for a significant transformation, with the National Capital Region Transport Corporation (NCRTC) signaling major advancements on multiple fronts. While the much-anticipated Meerut Regional Rapid Transit System (RRTS) project is on track for completion by June, the corporation is also pushing for crucial approvals for the Alwar and Panipat corridors within the year.
Addressing a press briefing, NCRTC Managing Director, [Insert MD’s Name if available, otherwise use “senior officials”], emphasized the corporation’s commitment to enhancing seamless and sustainable regional mobility. “Our vision is to create a robust, interconnected transportation network that reduces travel time, congestion, and pollution across the NCR,” they stated. “The Meerut corridor is nearing its final stages, and we are confident that the Alwar and Panipat corridors will receive the necessary approvals this year.”
Meerut RRTS: A Game Changer in Regional Commuting
The Delhi-Ghaziabad-Meerut RRTS corridor, India’s first semi-high-speed rail project, is nearing its operational zenith. The project, designed to significantly reduce travel time between Delhi and Meerut, is expected to be fully commissioned by June. The operational stretch, which has already seen passenger services, has received positive feedback from commuters, highlighting the speed and comfort of the trains.
“The Meerut corridor is a testament to our commitment to delivering world-class infrastructure,” the MD stated. “The project will not only improve connectivity but also stimulate economic growth along the corridor.” The RRTS trains, capable of reaching speeds of 180 kmph, are expected to drastically cut travel time between Delhi and Meerut to under an hour.
The remaining sections of the corridor are undergoing rigorous testing and commissioning procedures. The NCRTC is focusing on ensuring the highest safety standards and operational efficiency before opening the entire route to the public. Once fully operational, the Meerut RRTS is projected to carry lakhs of passengers daily, easing the burden on road infrastructure and reducing vehicular emissions.
Alwar and Panipat Corridors: Expanding the Regional Network
The proposed Alwar and Panipat RRTS corridors are crucial components of the NCRTC’s comprehensive plan to connect major urban centers in the region. The Alwar corridor, stretching from Delhi to Alwar via Gurugram and Rewari, will enhance connectivity between Delhi and Rajasthan, fostering economic and cultural exchange. The Panipat corridor, connecting Delhi to Panipat via Sonipat, will improve accessibility to Haryana’s industrial and agricultural heartland.
“The Alwar and Panipat corridors are vital for the future of the NCR,” the MD explained. “These projects will not only improve connectivity but also promote balanced regional development and reduce migration pressure on Delhi.”
The NCRTC is actively pursuing approvals from the relevant authorities, including the central and state governments. Detailed project reports (DPRs) have been submitted, and discussions are underway to address any outstanding issues. The corporation is optimistic that the necessary clearances will be granted within the year, paving the way for the commencement of construction.
Key Highlights of the Proposed Corridors:
- Alwar Corridor:
- Length: Approximately 107 kilometers.
- Route: Delhi-Gurugram-Rewari-Alwar.
- Expected Benefits: Improved connectivity with Rajasthan, boosting tourism and trade.
- Key Stations: Will include stations in major urban hubs along the route.
- Panipat Corridor:
- Length: Approximately 103 kilometers.
- Route: Delhi-Sonipat-Panipat.
- Expected Benefits: Enhanced connectivity with Haryana, supporting industrial and agricultural development.
- Key Stations: Will include stations in major urban hubs along the route.
Challenges and Future Outlook
While the NCRTC is making significant strides in expanding the regional transportation network, it faces several challenges. Land acquisition, environmental clearances, and funding are some of the key hurdles that need to be addressed. The corporation is working closely with the relevant authorities to expedite these processes and ensure the timely completion of projects.
Looking ahead, the NCRTC is committed to integrating the RRTS network with other modes of transportation, such as metro rail and bus services, to create a seamless and efficient multi-modal transit system. The corporation is also focusing on developing transit-oriented development (TOD) along the RRTS corridors, promoting sustainable urban growth and reducing reliance on private vehicles.
The successful implementation of the Meerut RRTS and the approval of the Alwar and Panipat corridors will mark a significant milestone in the development of the NCR. These projects will not only improve connectivity but also contribute to the economic and social well-being of the region. The NCRTC’s vision of a well-connected and sustainable NCR is rapidly becoming a reality, promising a brighter future for millions of commuters.